Ozone target control
Full control over target microcontroller- or microprocessor-based systems

Target control and communication
Ozone provides full control over a target via the debug interface. Control options include code stepping, breakpoint setting, and bi-directional terminal communication with target firmware. This enables users to examine a target system during every step of the debugging process.
Terminal communication
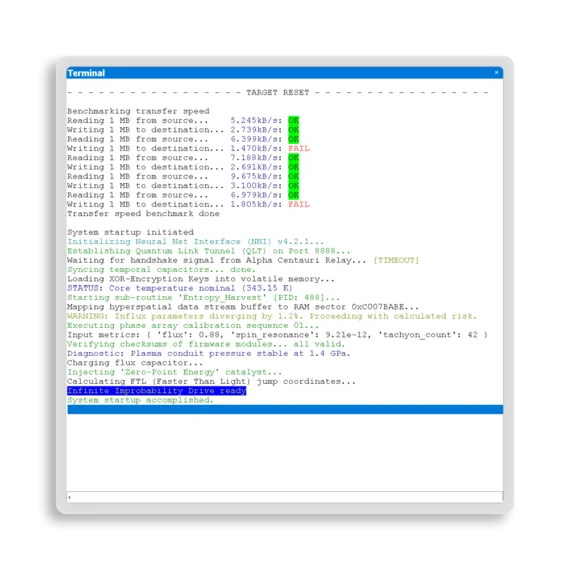
Ozone can communicate with target firmware using a terminal interface, and the firmware can push log and error messages into Ozone's terminal window. Firmware created for running specific tests can be controlled and return test results via the terminal interface.
User-interface peripherals not present during the debug process can be simulated using the terminal interface. Messages sent via Ozone can be used to simulate input devices. Messages sent by the target that would go to a display in the final product can be sent to the debugger during development.
To communicate, Ozone can utilize the Cortex-M SWO capability, semihosting, and SEGGER's Real Time Transfer (RTT) technology. RTT provides extremely fast IO coupled with low MCU intrusion.
Breakpoints for controlling program execution
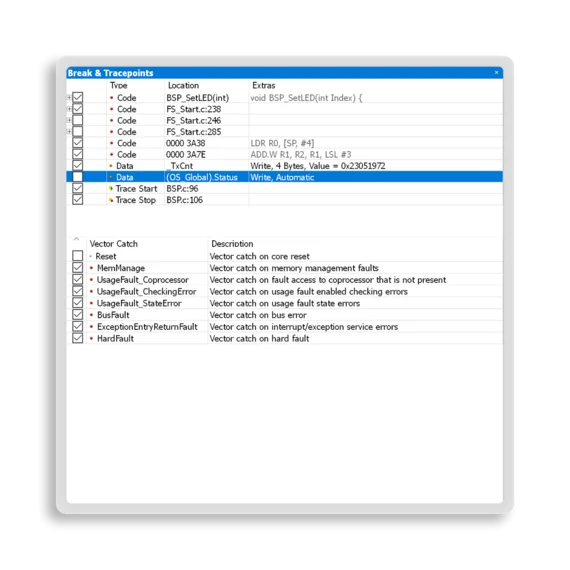
Breakpoints are a core debugging tool. Ozone supports code breakpoints at the source and instruction levels. Ozone users benefit from conditional breakpoints that assist in halting an application as required by the user, without the need to modify code.
If users need to examine a loop in a later iteration, they will set a skip count and tell Ozone to automatically skip a breakpoint a specified number of times, which relieves them from counting and stepping manually. Similarly, an iterative skip count can be used to halt every other occurrence.
In situations where a function is called from a multitude of places in an application, it can be helpful to stop the firmware only if it is called from a specific task. Ozone can offer the required condition, if an RTOS-awareness plugin is active.
In addition, Ozone can even evaluate complex conditions each time a breakpoint is hit, in order to determine whether control is passed to the user or execution is continued to the next breakpoint. The evaluation can also use RTOS awareness.
Finally, Ozone benefits from J-Link's unlimited flash breakpoints.
Data breakpoints
To monitor memory locations important to the program flow, users can set data breakpoints. These trigger a program halt every time memory location is accessed. Conditions for determining whether a data breakpoint should trigger a halt include memory address/area, access type (read/write), access size, and value. This aids in detection of unwanted memory access or memory access that does not yield an expected result. In addition, both stack overflows and heap-use-after-free can be identified.
Examination of program flow with stepping
Ozone provides the following standard step modes: single step to the next line, step into a function, step over a function, and instruction-level stepping. If users want to temporarily exclude functions from execution, they can simply move the program counter to the next code line and continue execution.
For one-time inspection of a state at a specific location, users can place the cursor at that location and chose the run-to-cursor mode, which lets the application run to the specified location.